Polarization of Light
Problem 5.188
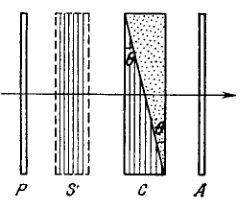
Light with wavelength falls on a system of crossed polarizer and analyzer between which a Babinet compensator is inserted (Fig. 5.33). The compensator consists of two quartz wedges with the optical axis of one of them being parallel to the edge, and of the other, perpendicular to it. The principal directions of the polarizer and the analyser form an angle of with the optical axes of the compensator. The refracting angle of the wedges is equal to and the difference of refractive indices of quartz is The insertion of investigated birefringent sample with the optical axis oriented as shown in the figure, results in displacement of the fringes upward by . Find: (a) the width of the fringe ; (b) the magnitude and the sign of the optical path difference of ordinary and extraordinary rays, which appears due to the sample