Mechanical Oscillations
Problem 4.65
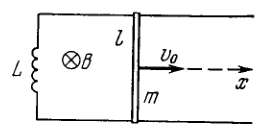
A loop (Fig. 4.23) is formed by two parallel conductors connected by a solenoid with inductance and a conducting rod of mass which can freely (without friction) slide over the conductors. The conductors are located in a horizontal plane in a uniform vertical magnetic field with induction The distance between the conductors is equal to At the moment the rod is imparted an initial velocity directed to the right. Find the law of its motion if the electric resistance of the loop is negligible.