Interference of Light
Problem 5.77
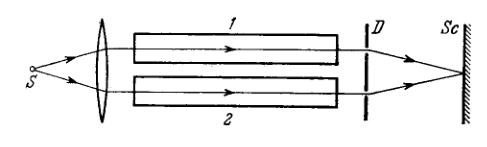
Figure 5.16 illustrates an interferometer used in measurements of refractive indices of transparent substances. Here is a narrow slit illuminated by monochromatic light with wavelength and 2 are identical tubes with air of length each, is a diaphragm with two slits. After the air in tube 1 was replaced with ammonia gas, the interference pattern on the screen was displaced upward by fringes. The refractive index of air is equal to . Determine the refractive index of ammonia gas.