Second law of thermodynamics, entropy
Problem 2.116
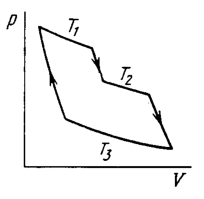
An ideal gas goes through a cycle consisting of alternate isothermal and adiabatic curves (Fig. 2.2). The isothermal processes proceed at the temperatures and Find the efficiency of such a cycle, if in each isothermal expansion the gas volume increases in the same proportion.