Equation of the gas state processes
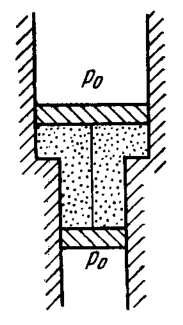
Problem 2.10
A smooth vertical tube having two different sections is open from both ends and equipped with two pistons of different areas (Fig. 2.1). Each piston slides within a respective tube section. One mole of ideal gas is enclosed between the pistons tied with a non-stretchable thread. The crosssectional area of the upper piston is greater than that of the lower one. The combined mass of the two pistons is equal to . The outside air pressure is atm. By how many kelvins must the gas between the pistons be heated to shift the pistons through